Blog
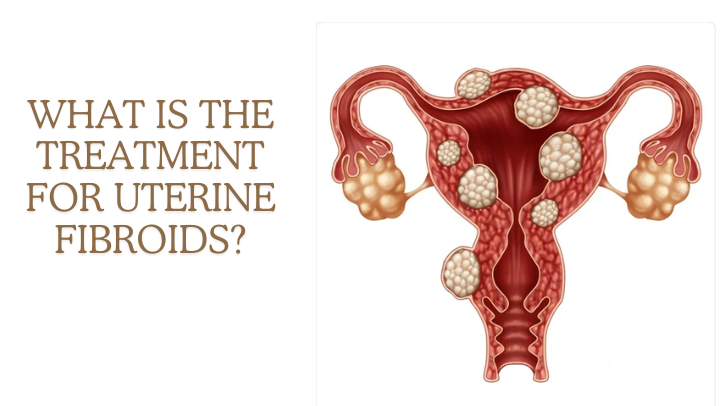
What Is The Treatment For Uterine Fibroids? Uterine Fibroids, also known as Leiomyomas, (lie-o-my-O-muhs) smooth muscle tumors, Because smooth muscle is an extrinsic muscle, most leiomyomatas are found in the viscera. Most commonly, they are found in the uterine lining, in the muscular and submucosal layers of the digestive system, gallbladder, or in the smooth muscles of the skin. Fibroids are a very common type of muscle or tissue growth that develops inside or on the walls of the uterus. Most uterine fibroids are not cancerous. It often appears during the pregnancy period or when you’re usually able to get pregnant and give birth. Fibroids affect roughly 40% and 80% of women aged 30 to 50. Women who have not gotten their first period do not usually develop fibroids. Fibroids are also less common in women who have gone through menopause.
Typically, fibroids are small, round, smooth bumps. Some fibroids may have a thin stem attached to them, giving them the appearance of a mushroom. Fibroids can grow individually or in clusters. For comparison, Fibroids can range in size from as little as a seed to as much as a large watermelon. They can grow inside the uterine wall, in the main uterine cavity, or even on the outside of the uterus.
The cause of fibroids is not fully understood, but healthcare providers think it may be related to the hormone levels of estrogen and progesterone. The majority of fibroids occur in women of reproductive age. Research has shown that fibroids increase when estrogen is present (e.g., during pregnancy) and decrease when estrogen levels are low (e.g. during menopause).
If your fibroids are small, you may not feel anything at all and may not even be aware of them. However, if they are large, you may experience pain and discomfort. Uterine fibroids typically resolve or disappear after menopause due to a decrease in hormone levels in the body. Fibroids do not always lead to symptoms, but if they do, they can include:
Fibroids are often diagnosed during a pelvic examination. In many cases, severe bleeding and other symptoms may prompt your doctor to include fibroids in the diagnosis. Several tests can be used to confirm the presence of a fibroid and determine the size and location of a fibroid. These tests can include:
While small fibroids usually do not require treatment, bigger fibroids may require treatment with drugs or surgery and depend upon –
Uterine fibroid drugs target hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle. These drugs treat symptoms like heavy periods and pelvic pressure. While they do not remove fibroids, they may reduce the size of them. Uterine fibroid medicines include:
If you are looking for Uterine Fibroids or any other medical Assistance Dr Ruchi Rai Ahuja is an expert gynaecologist. Book an appointment for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Copyright © 2026 Dr Ahuja Clinic. All Rights Reserved | Marketing by : WebHopers
Website Design by CSW Technologies